Ethereum vs Ethereum 2.0: What’s the Difference?
Ethereum launched in 2015 as a proof-of-work (PoW) blockchain platform that empowered developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) and issue tokens. Rapid adoption unveiled challenges: limited transactions per second (TPS), rising gas fees, and high energy consumption. Ethereum 2.0 (often called “Eth2” or “the upgrade”) addresses these issues through a shift to proof-of-stake (PoS), paving the way for greater scalability, security, and sustainability. This article unpacks what changed in Ethereum’s “The Merge” and what lies ahead.
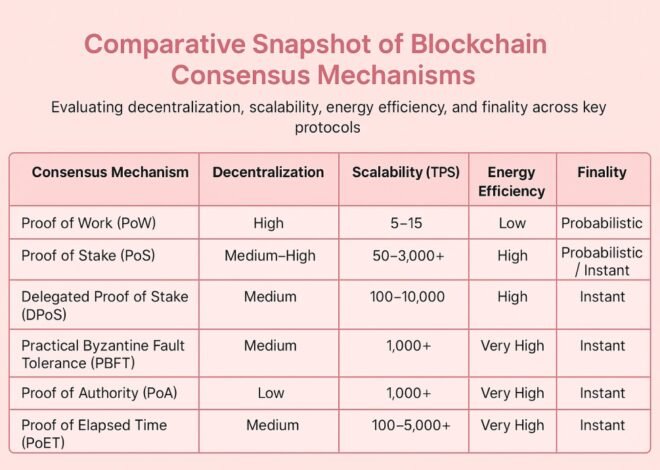
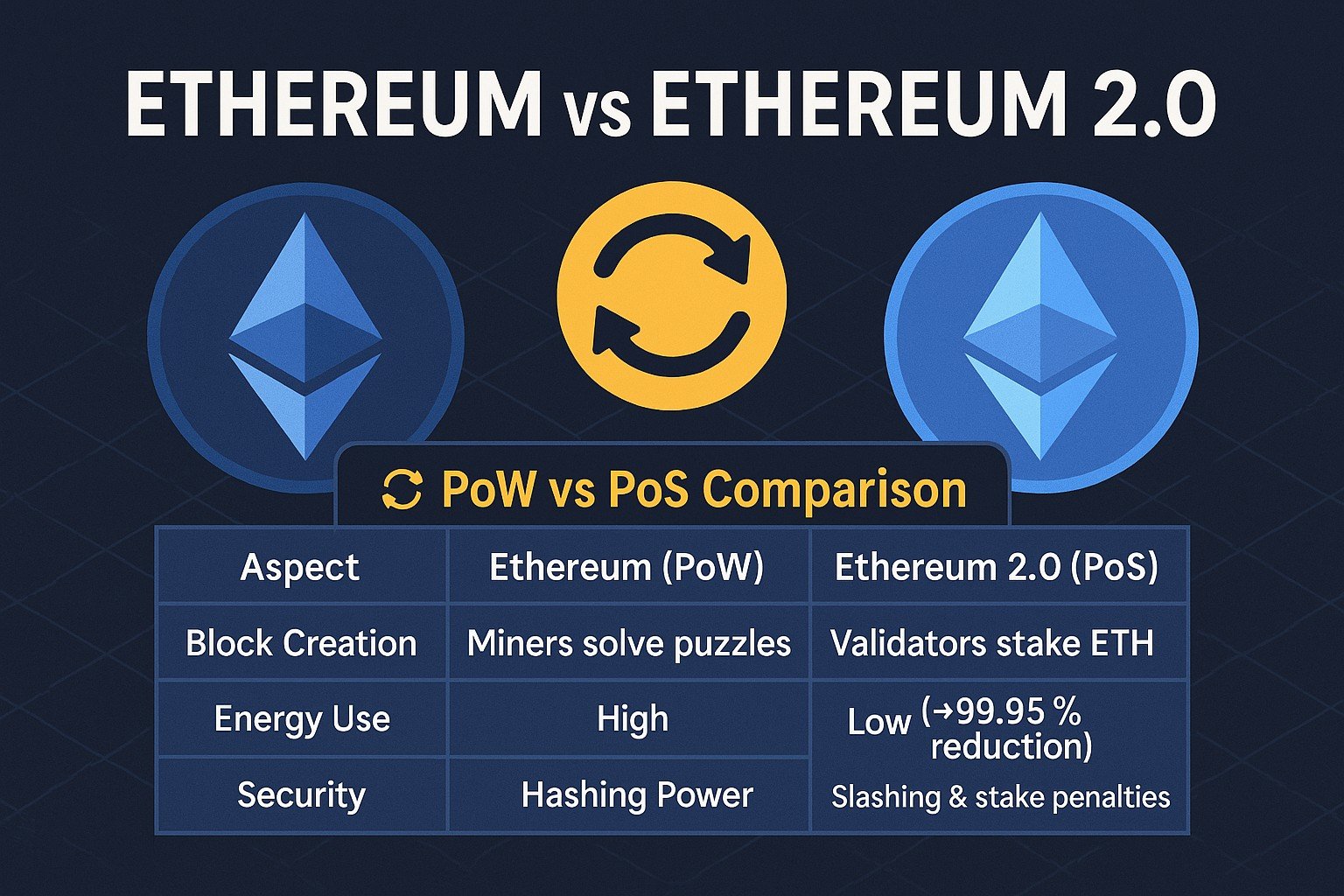
Consensus Mechanism: PoW vs PoS
Proof of Work (Ethereum Legacy)
- Miners race to solve cryptographic puzzles.
- High energy demand; specialized hardware dominates.
- Security relies on hashing power deterrence.
Proof of Stake (Ethereum 2.0)
- Validators lock up ETH (“stake”) to propose and confirm blocks.
- Energy consumption drops by ~99.95%.
- Economic penalties (“slashing”) discourage malicious behavior.
Energy Efficiency
Ethereum’s PoW model consumed energy comparable to a small country, fueling environmental concerns and centralization in mining pools. Ethereum 2.0’s PoS consensus eliminates competitive mining, cutting power usage dramatically and reducing barriers to entry. This transition not only appeals to eco-conscious developers and enterprises but also aligns blockchain adoption with global sustainability goals.
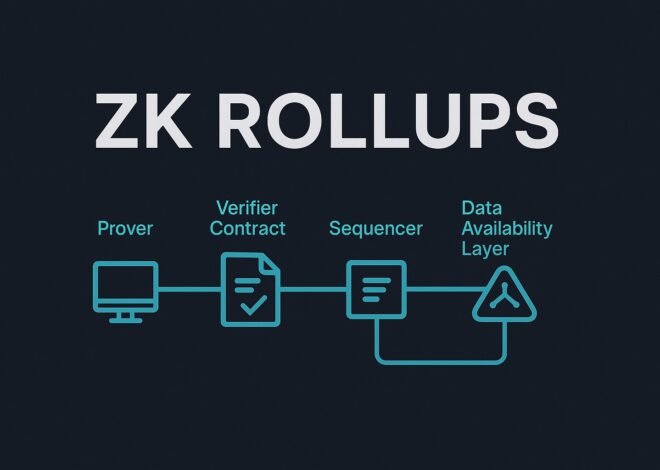
Scalability and Throughput
Under PoW, Ethereum processed roughly 15–30 TPS, leading to network congestion and unpredictable fees. Ethereum 2.0 introduces:
- Sharding (future upgrade): Splits the blockchain into 64 parallel chains to multiply capacity.
- Rollups (already in use): Bundle transactions off-chain and settle proofs on Ethereum’s mainnet.
Together, these layers aim to boost aggregated throughput to thousands of TPS, slashing costs and latency.
Security and Economic Incentives
PoW security hinges on hashing power: attackers need over 51% of mining hash rate to disrupt consensus. PoS shifts this model—validators stake ETH, and an attacker must amass over 51% of staked ETH at enormous cost. Misbehavior triggers slashing, where malicious or offline validators lose a portion of their stake. This economic alignment promotes network integrity and long-term participation.
Token Economics
Ethereum’s original issuance schedule rewarded miners with block subsidies and transaction fees, fueling inflationary pressure. Post-Merge, Ethereum’s issuance rate dropped by ~90%, as block rewards shifted from miners to stakers. Combined with EIP-1559’s burning mechanism (introduced in 2021), Ethereum now trends toward deflation when network activity is high, potentially increasing scarcity and value over time.
The Merge: Milestone Achieved
On September 15, 2022, Ethereum executed “The Merge,” uniting the original PoW chain with the Beacon Chain PoS system. The transition was seamless for dApp developers and users—no code rewrites were needed, and all smart contracts, wallets, and balances remained intact. The Merge stands as a landmark, proving a major blockchain can overhaul its consensus without network disruption.
Future Roadmap for Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0 continues to evolve beyond the Merge. Key upcoming upgrades include:
- Sharding: Launching shard chains to parallelize data processing.
- Verkle Trees: Advanced data commitments to reduce node storage requirements.
- Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844): Lower rollup costs via temporary blob storage.
These enhancements collectively boost performance and lower costs for developers and end users.
Impact on Developers and Users
For developers, Ethereum 2.0 means:
- No changes to existing smart contracts or tooling.
- Access to cheaper, faster transaction settlement—ideal for complex DeFi and NFT applications.
For users, the upgrade offers:
- Staking opportunities that yield passive ETH rewards.
- Lower and more predictable gas fees as scaling solutions roll out.
Conclusion
Ethereum 2.0 represents more than a simple upgrade—it’s a paradigm shift toward a sustainable, high-throughput, economically robust blockchain. By moving from PoW to PoS, slashing energy consumption, and laying groundwork for sharding and rollups, Ethereum is primed for mass adoption and innovation. The future of decentralized finance and beyond will hinge on these foundational changes, making Ethereum 2.0 the blueprint for next-generation blockchain architecture.